Colonoscopy Flow
1. Preparation on the day before examination
The day before the colonoscopic examination, the clinic will provide you with a retort examination meal (breakfast, lunch, and dinner) that is easily digestible and low fiber diet.
*If you are very hungry, it is possible to have an easy-to-digest meal such as plain udon.
Before bedtime, the patient is required to take a laxative prescribed by the clinic.
2. Preparation for the day
On the day of the colonoscopy, the patient will take a medicine that stimulates the movement of the intestinal tract, and 30 minutes later, A Bowel-cleansing solution will be taken slowly within about an hour.
*A Bowel-cleansing solution do not cause abdominal pain and are safe to drink.
*Sometimes patients say, “The examination was easy, but it was hard to drink the bowel-cleansing solution.

We have devised a patient-specific dosage regimen to reduce the burden of drinking bowel-cleansing solutions.
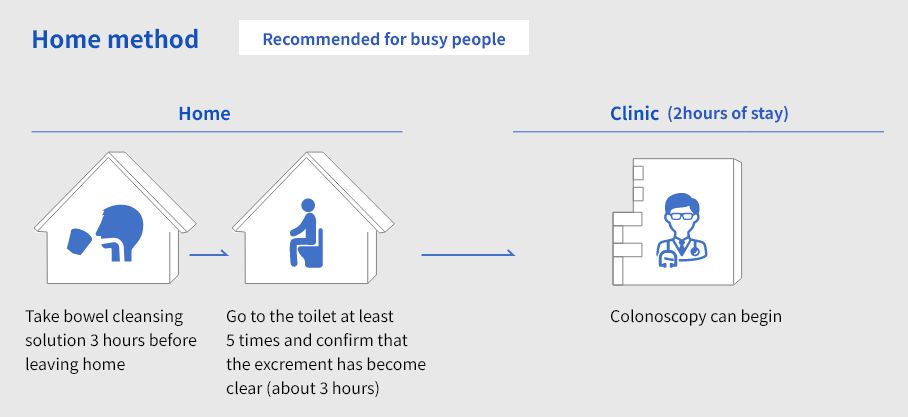
- Home method
- A method in which the patient takes bowel-cleansing solution at home and comes to the clinic with a clean intestine.
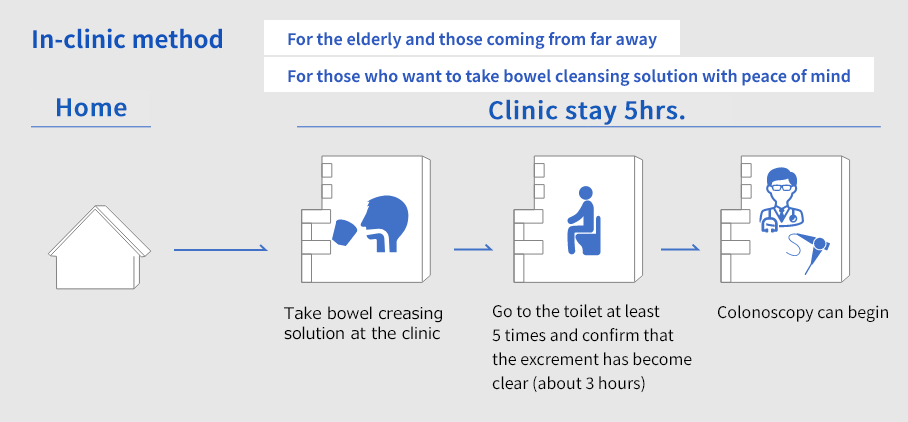
- In-Clinic Method
- For patients who come to the clinic from a distance or are elderly, the bowel cleansing solution is administered at the clinic.
- Infusion method
- This is a method in which approximately 1.0L (500ml of bowel cleansing solution + 500ml of water) is infused into the stomach or duodenum during gastro endoscopy.
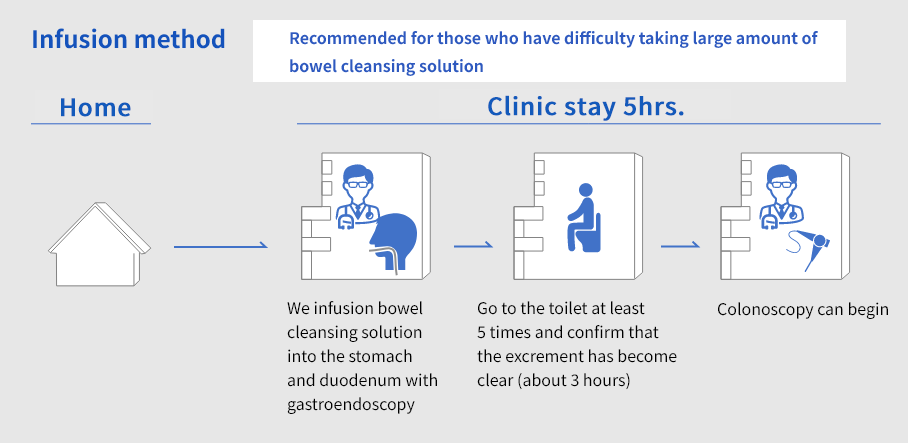
3.Colonoscopy flow
The patient lies down on the examination table and is given a mild sedative intravenously. The colonoscope is then inserted through the anus to the cecum.
The advanced technique of inserting the colonoscope in a straight line through the approximately 1.5-meter long intestinal tract of the large intestine, like folding an accordion, allows the examination to be completed quickly and without causing the patient any pain at all.
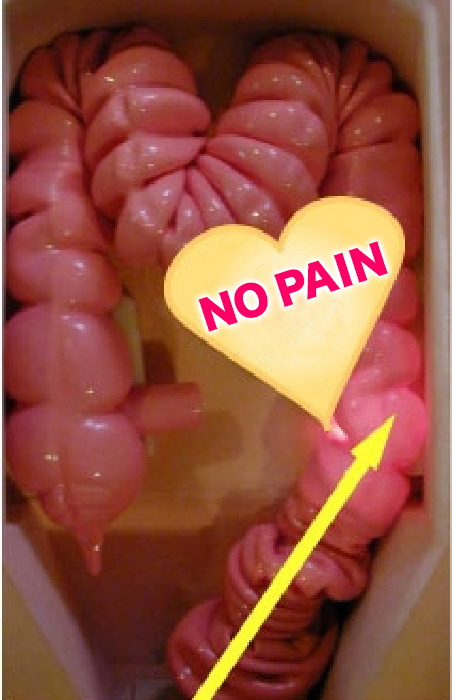
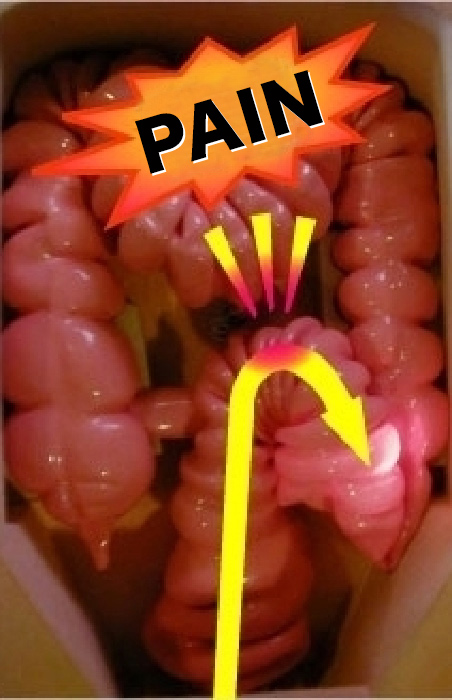
On the other hand, when the intestinal tract is stretched, as in the picture, it causes pain. Thus, advanced colonoscopic techniques that do not stretch the intestinal tract help reduce the burden on the patient. Examinations using anesthetic agents can cause great danger to the body because the patient does not feel pain when the intestine is injured or when the intestinal tract is stretched.
Therefore, caution should be exercised in completely sleepy examinations with the use of anesthetic agents.
4.After the colonoscopy
Since the injections and medications used in the colonoscopy may cause you to feel lightheaded, you will lie down in a private room to rest for about 30 minutes after the colonoscopic examination.
Please do not drive a car after the examination, as it is very dangerous.
Notes
- If you are taking medications that prevent blood from clotting (anticoagulants pediatric bufferin, warfarin, panardin, etc.), it will be difficult to stop the bleeding. For this reason, we used to ask patients to stop taking the medication 3 days prior to the examination, but due to the adverse effects of such discontinuation, we now ask patients to continue taking the medication without discontinuation. If you have polyps removed, please be assured that the wound will be colonoscopically sutured completely.
-
On the day of the examination, please take your usual medications (blood pressure, heart, asthma medications, etc.) early in the morning (around 8:00).
(However, please do not take diabetic insulin injections or oral diabetic medications on the day of the examination.) - If you feel thirsty on the day of the examination, you may drink water.
- If you feel hungry, please eat candy or gum.
Regarding bowel cleansing
In order to find small cancers and difficult-to-detect lesions such as depressed type cancer, the colon must be cleaned.
If stool remains in the colon, it is even more difficult to detect depressed type cancers and other lesions hidden by retained stool.
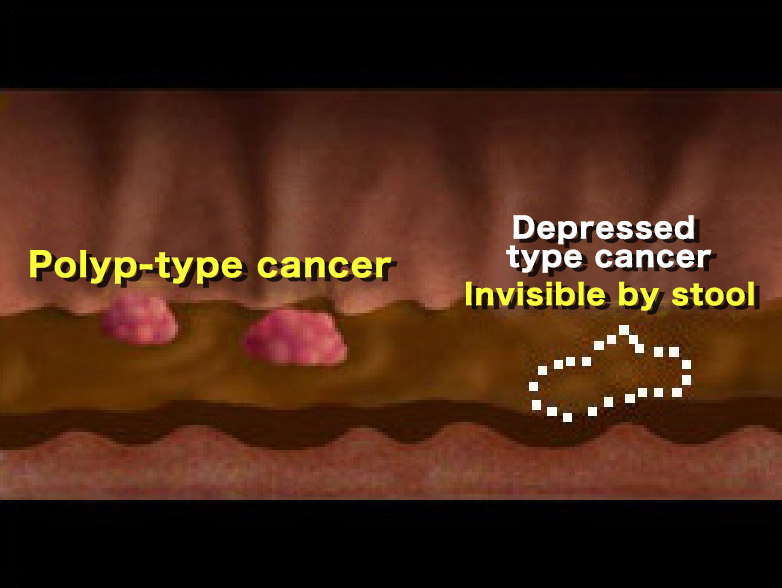
Polyp-type cancers can be detected, but depressed-type cancers can be more difficult to detect.
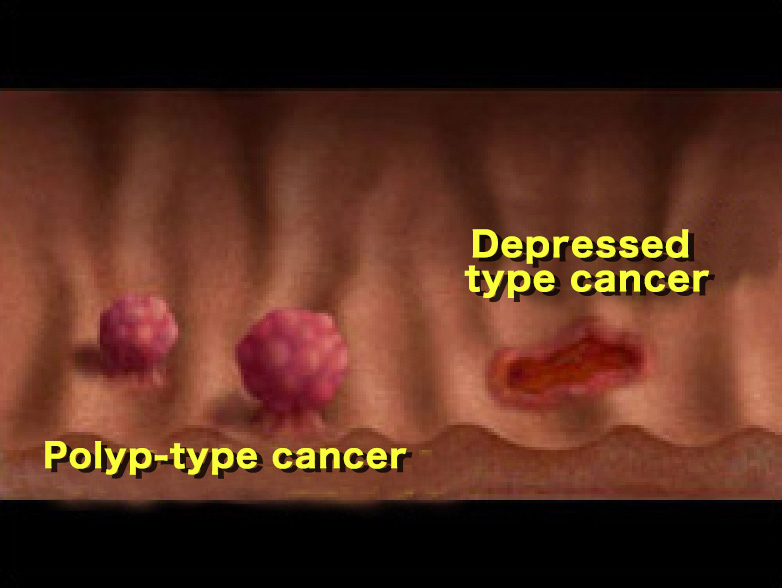
It is easier to detect polyp-type cancers as well as depressed-type cancers, which are difficult to detect.
What cancers can be found by colonoscopy?
Traditionally, the cause of colorectal cancer was thought to be polyps that protrude in a warty shape, so the field of endoscopy has focused its energies on finding and removing polyps. On the other hand, unlike polyps, depressed type lesion can easily become cancerous at a fast rate, and even cancers smaller than 10 mm can metastasize.
This type of depressed cancer is considered a lesion that is difficult to detect and easily overlooked, and has been considered by Western colonoscopists to be a disease unique to the Japanese.
The Director spent four months in the U.K. from 1995 as a Japan-U.K. Collaborative Research Fellow to provide endoscopic guidance, and discovered the first two cases of depressed-type cancer in U.K. patients, which were reported in academic societies and English journals. Currently, depressed type cancer is attracting attention internationally.
Our clinic strives to avoid overlooking depressed-type cancers, which are notoriously difficult to detect, and our goal is to provide reliable diagnosis and treatment.

First case of depressed type cancer discovered in the UK.

Endoscopic image of the first depressed type cancer detected in an English person.
A lesion detected by focusing on faint reddish mucosal changes, a lesion that is generally missed.
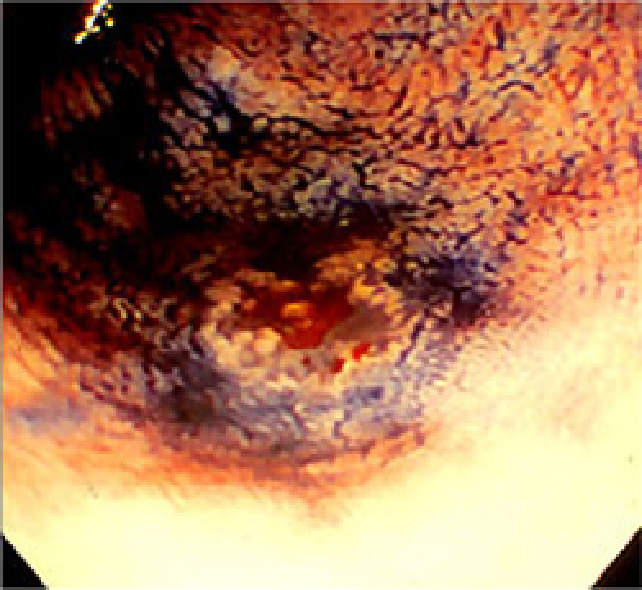
Same lesion after dye spraying

The dye can be used to identify the lesion as a depressed lesion.
The lesion was completely removed by colonoscopic treatment.
Diagnosis of depressed type cancer
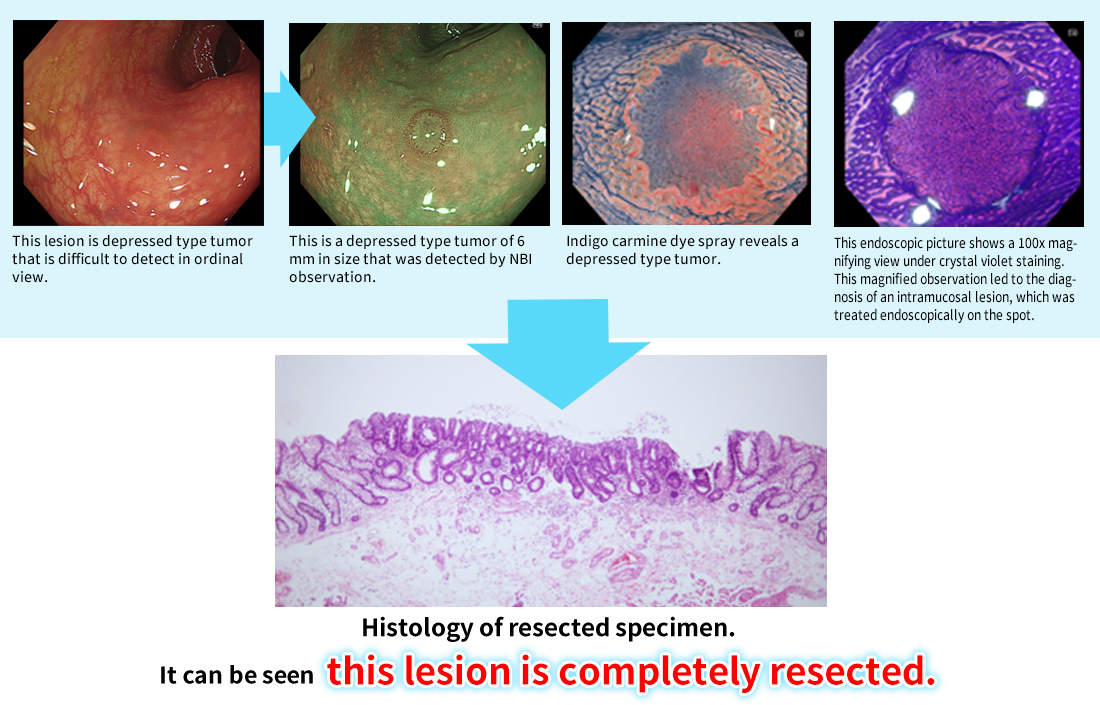
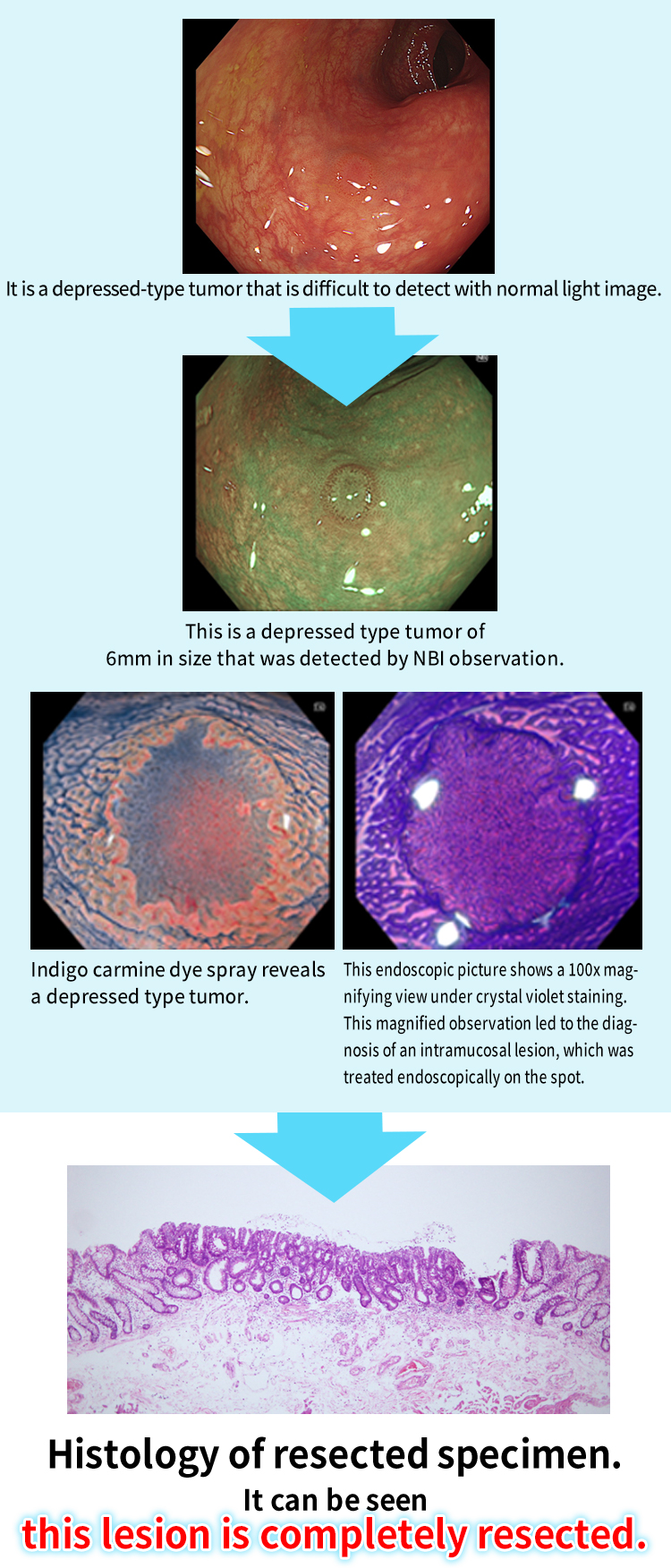
Depressed type tumor (IIc) of 6mm in size found in our clinic.
We use a high-definition magnifying colonoscope to detect depressed type tumors with the special light of NBI.
Such cancers do not test positive in the fecal occult blood test. Moreover, they are difficult to detect by barium enema or CT colonography.
The detection of such depressed-type cancers requires a clean intestinal tract and highly accurate endoscopic examinations techniques.
Day surgery
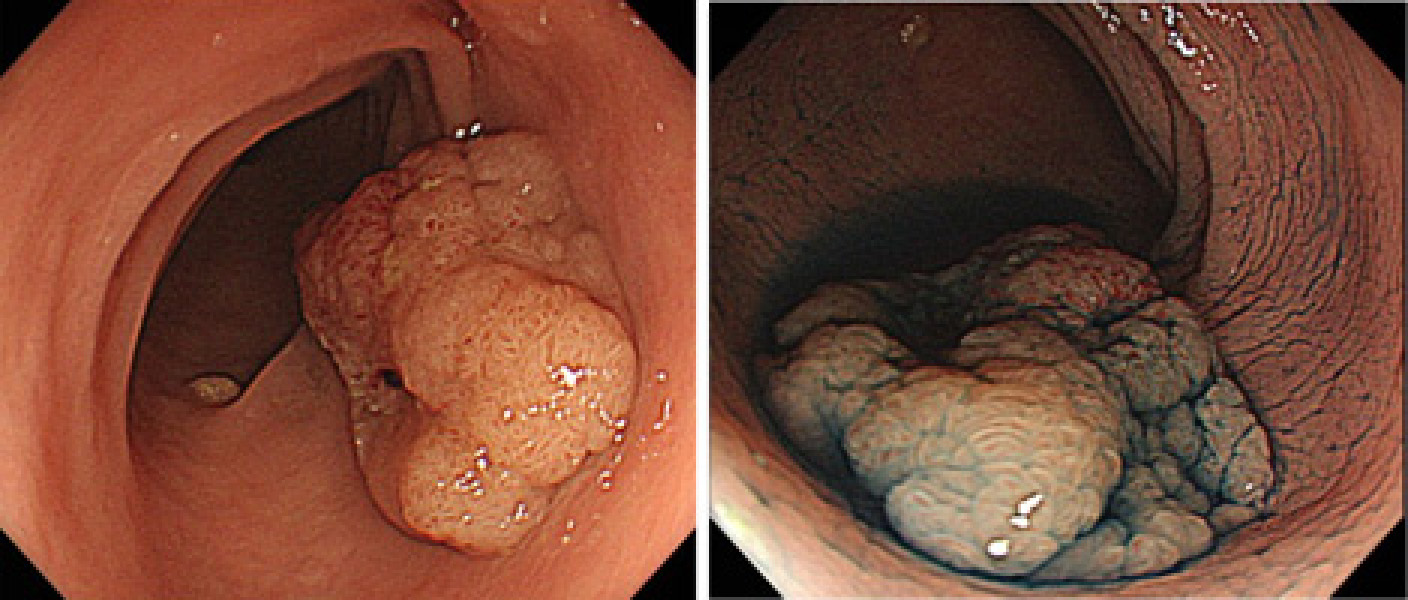
A lesion 30mm in size in the sigmoid colon that was considered open surgery at another hospital. It is a neoplastic lesion in which the presence of cancer is suspected in some of the polyps.

In general hospital facilities, a biopsy of a portion of the lesion is taken, and based on the pathology results, endoscopic treatment may be performed after hospitalization, or surgery may be performed.
We performed NBI, injigocarmine dye, and Crystal violet staining, and based on endoscopic observation magnified 100 times, diagnosed the patient as having early-stage cancer that remained within the intramucosa. We determined that endoscopic mucosal resection was indicated instead of the surgical procedure recommended by the previous physician, and endoscopic resection could be performed during that examination.
The wound after resection was completely sutured, and the patient was able to return home safely after the day surgery, with no further complications observed.
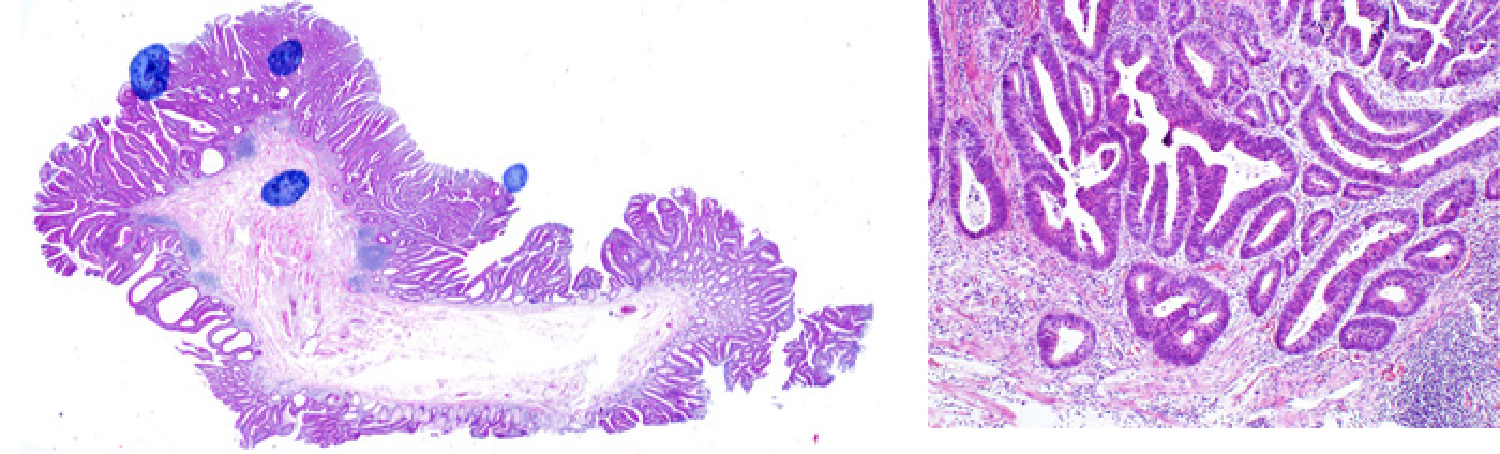
Endoscopically resected histology. As diagnosed by endoscopy, the patient had an extremely early-stage cancer that remained within the mucosa, although well differentiated adenocarcinoma was observed in some parts of the tumor.
The lesion was completely resected, there was no concern about metastasis, and the lesion was judged to be completely cured.
We have accurate diagnostic capabilities and techniques, including the use of magnifying colonoscopy to diagnose benign and malignant polyps.
Therefore, from diagnosis to treatment can be completed in a single examination, which is what makes our clinic unique.